Export tasks (legacy)
We generally do not recommend using export tasks to write data back to external sources. However, export tasks may be available and supported for some source types based on your Foundry enrollment.
The following export task documentation is intended for users of export tasks who have not yet transitioned to our recommended export workflow.
Overview
Export tasks allow you to export data from Foundry to various external data sources. The configuration for an export task consists of two parts:
- Source: Defines how the agent connects to the data source. Should be configured the same way as for dataset syncs.
- Task configuration: Defines the type of export, input datasets, and parameters for the export.
An export task is triggered when a job is started on the task output dataset.
Known export task limitations
- Export tasks are not integrated with markings and export controls. Data exported via export tasks do not require unmarking permission on the exported dataset or stream.
- Export tasks are not optimized for performance. Exporting large quantities of data may result in long-running jobs or jobs that fail to complete.
- Export tasks do not have a user interface for configuration and instead must be configured using YAML to provide the required configuration options. Not all export task options are documented for self-service use; in some cases, export tasks can only be configured through support from Palantir.
- Export tasks only work on agent-worker sources.
Getting started
To configure an export task:
- Configure a source in Data Connection to connect to the target system where you are exporting.
- In the Foundry file system, navigate to the folder containing the source. Right-click on the resource and select Create Data Connection Task.
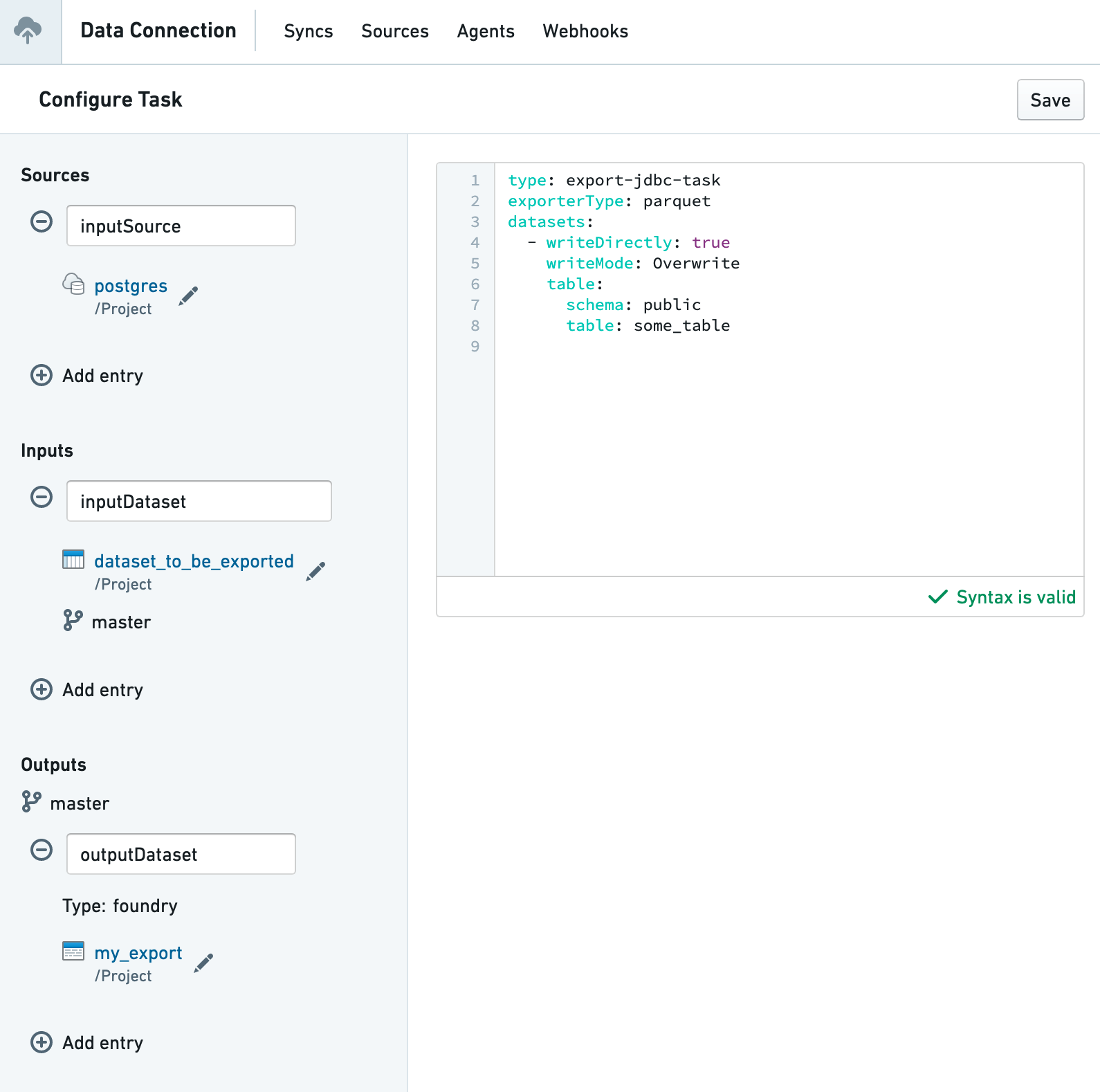
- In the Task Editor UI:
- Keep the source named
inputSource - Add an input dataset named
inputDataset - Create or choose an output dataset named
outputDataset - Configure the YAML for your specific export type
- Keep the source named
The input source must be named inputSource and the output dataset must be named outputDataset. Failure to use these specific names may result in task errors.
Supported export types
Data Connection export tasks support writing to a wide range of common enterprise systems:
- Amazon S3
- OneLake and Azure Blob Filesystem (ABFS)
- HDFS
- JDBC-compatible systems, including:
- Relational databases
- Data warehouses
- Teradata
- Snowflake
- Vertica
- File systems, including network file systems mounted on the intermediary agent
- SFTP
Common configuration options
Incremental exports
All export types support the incrementalType parameter, which controls how data is exported over time. For JDBC exports, this parameter is specified per dataset rather than globally.
When set to snapshot (the default value), the export task exports all files visible in the current view of the input dataset. This means every export will include the complete dataset, regardless of what was previously exported.
When set to incremental, the export behavior changes to optimize for efficiency. The first export behaves like a snapshot, exporting all available data. On subsequent exports, only new transactions added since the last export will be included, provided the initial exported transaction is still present in the dataset. If the initial transaction is no longer available (for example, due to a dataset rebuild), the system automatically falls back to a full snapshot export.
Example for file-based exports:
Copied!1incrementalType: incremental
Path rewriting
File-based exports support the rewritePaths configuration option for customizing file names and paths during export. This field accepts a map of regular expressions and substitution templates:
Copied!1 2rewritePaths: "^spark/(.*)": "$1" # Removes the spark/ prefix
The substitution templates support several dynamic replacement patterns:
- regex capture groups such as
$1,$2, and so on to reference matched portions of the original path. - timestamp patterns like
${dt:yyyy-MM-dd}, which use Java's DateTimeFormatter syntax to insert the current date and time. - Foundry transaction ID using
${transaction} - Foundry dataset ID using
${dataset}