- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Ontology permissions
Project-based permissions are in the beta phase of development and may not be available for your enrollment. Functionality may change during active development.
You may also review the legacy documentation on previous ontology permissions models.
The permissions to view, edit, and manage ontology resources are managed through Compass, the Palantir platform's filesystem.
Currently, this feature must be manually enabled and existing ontology resources require migration.
This project-based permissions approach replaces the previous permission models: ontology roles and datasource-derived permissions. It comes with multiple benefits:
- Unified permission model: Ontology resources now use the same permission system as other resource types, so you only need to learn and manage permissions in one place.
- Bulk management: Set permissions at the folder or project level to control access across multiple resources at once, eliminating the need to set permissions on individual items.
- Clearer visibility: The Security tab and sidebar now display permissions and project context for all resources, including ontologies.
- Increased functionality: As project resources, ontologies gain access to Compass features like folders, access requests, markings, and tags.
Example of project-based permission
For example, consider an object type called Building, now saved as a file in project A. Your ability to view, edit, or manage Building depends on your role in project A. If you are an Editor in project A, you can edit the Building object type. To view specific Building objects (like Empire State Building), you need the Viewer role on both the object type and its datasource.
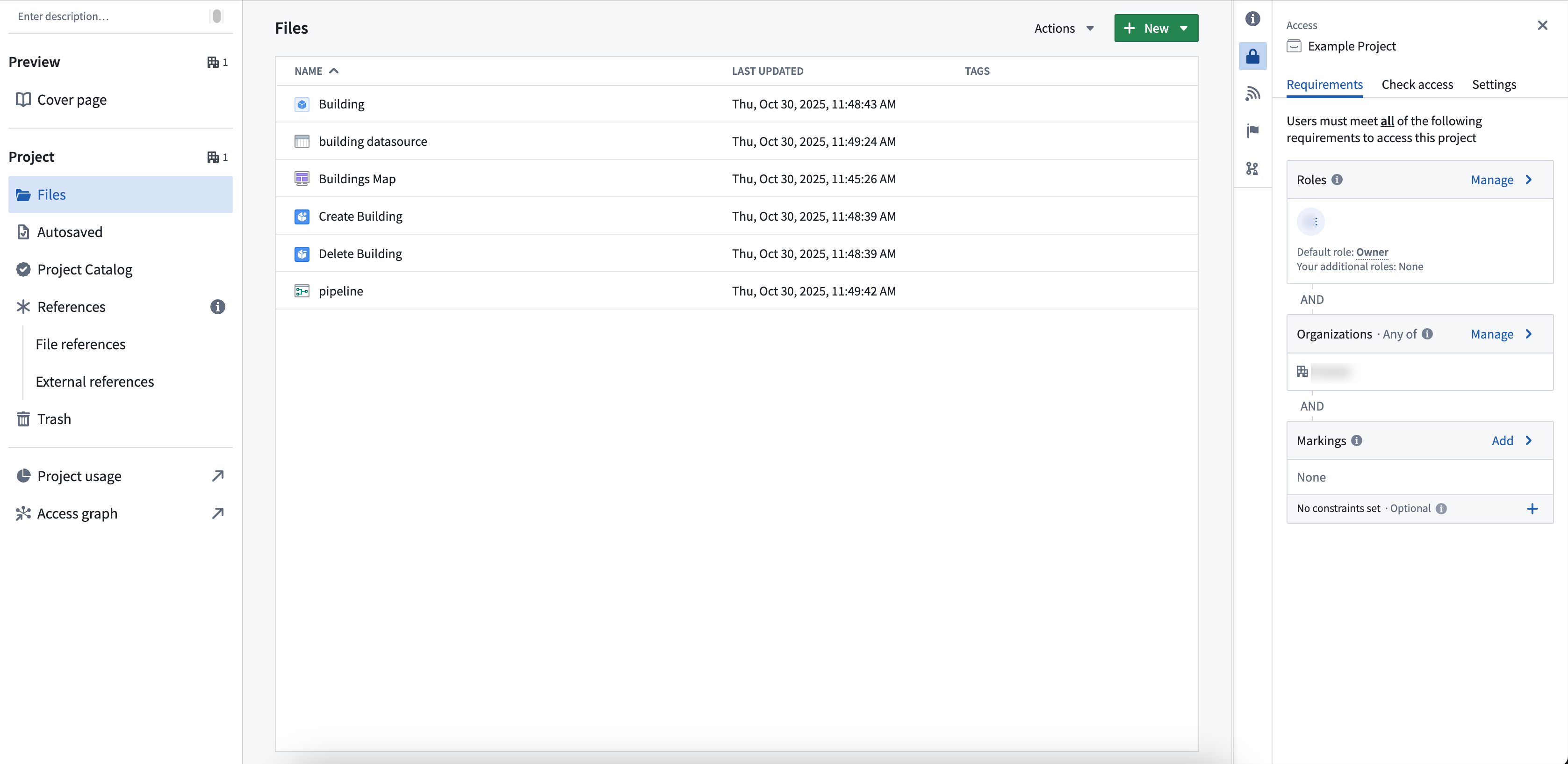
If you only have viewing rights for the object type, you can only see information such as schema and contact information, not the actual data. If you need help understanding the permissions required, review the Compass project side panel.
Viewing object types and objects
Object types are permissioned differently from objects. To see an object type, you must have View permissions on the object type, but do not need View permissions for the backing datasource.
To see objects, you must hold View permissions on both the object type and the backing datasource.
For more information on the distinction between object types (schema) and objects (data), review the documentation on object permissions.
Edit permissions for links and actions
You will need the appropriate edit permissions depending on the resource you would like to edit:
- For links: You must hold edit permissions on both the link type and the linked object types.
- For actions: You must hold edit permissions on the action type and on all ontology resource types edited by the action.
Previous permission models
Previously, permissioning ontology resources varied based on your ontology authorization model. The table below summarizes how resources are currently managed for each model. Refer to the documentation to learn more about these legacy permission systems.
| Legacy Ontology permission models | Description |
|---|---|
| Ontology roles | - Ontology resources are permissioned in Ontology Manager using ontology specific roles (Ontology viewer, Ontology editor, and Ontology owner). They are not a resource of a project. |
| Datasource-derived | - Ontology resources derive their permissions from the backing datasource of the object. For example, you have editor on the object type if and only if you are editor on the backing datasource. |