- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Map Search Arounds
Search Arounds are link or function-based searches that allow users to explore related objects.
Link Search Arounds
A user can Search Around from any geospatial object to any geospatial objects it is linked to. See Create a link type for more information.
Link merged Search Arounds
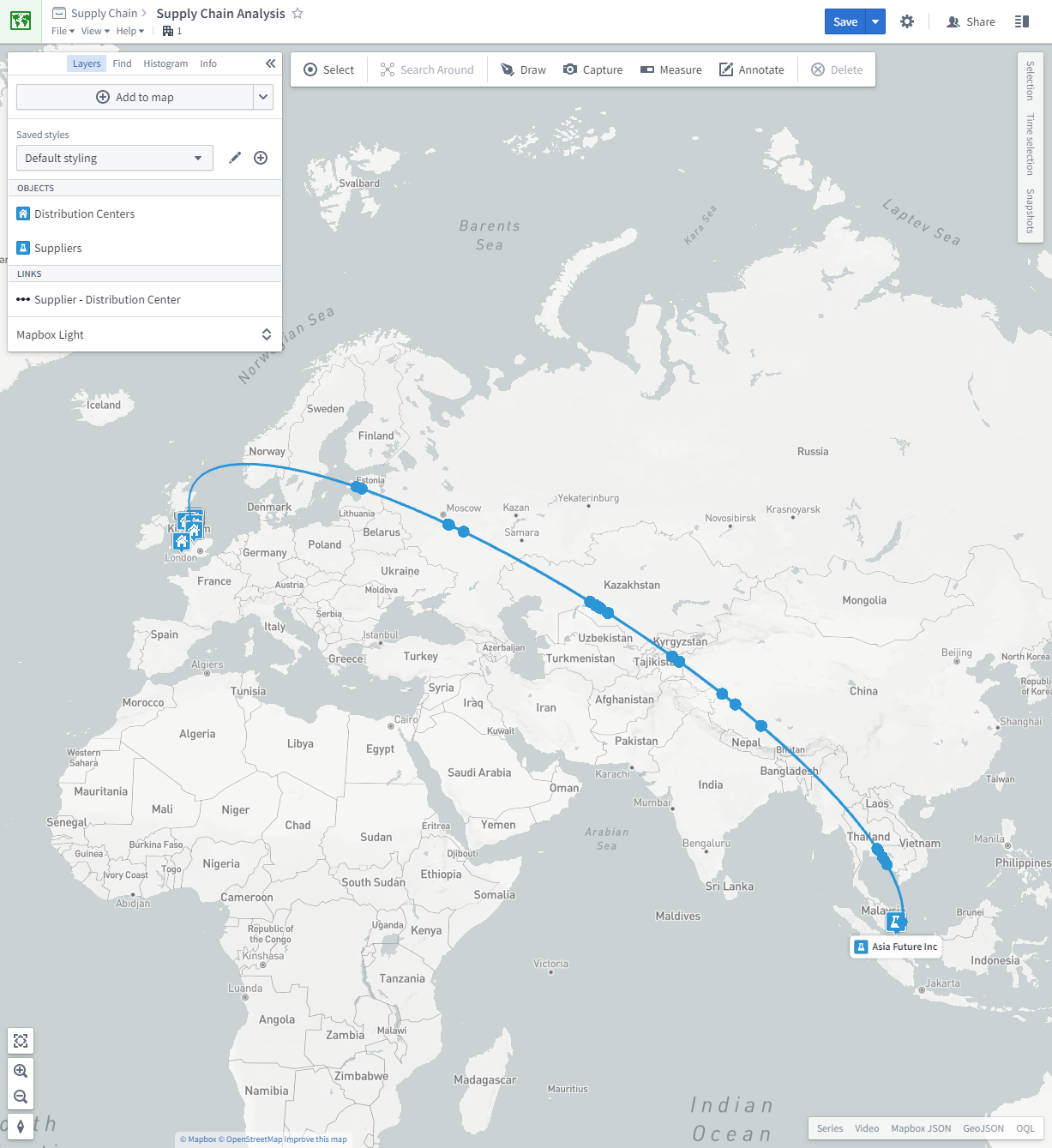
The Map application can run two-step Search Arounds, where a geospatial object is linked to another geospatial object via an intermediary object (which could be non-geospatial).
- The intermediary object might represent a relationship between the two objects. For example, a
Factoryobject and aSupplierobject might be related via aSupply Contractobject; when a Search Around is run, the Map will show an arc from factory to supplier, where the arc represents the supply contract. - The intermediary object might also be an event which both objects are involved with. For example, a
Customerobject might be linked to aDistribution Centerobject via aDeliveryevent - in this case, the delivery events will be shown as circles traveling along the arc. The position of the circle will be interpolated along the arc based on the event start and end time as well as the currently selected timestamp.
There are two methods for configuring objects to be used for link merged Search Arounds:
- Designating the intermediary object as a link merge object, which means that this object type itself will never appear in the Search Around list, but its transitive links will.
- Designating specific link traversals to be merged. Use this approach if only some of the relations of the intermediary object should be link merged.
Set an intermediary object type to always link merge
To designate an intermediary object type to always link merge, turn on Link merge always in the Search Around section of the intermediary object type's Capabilities tab. This means that the object type itself will never appear in the Search Around list, but its transitive links will.
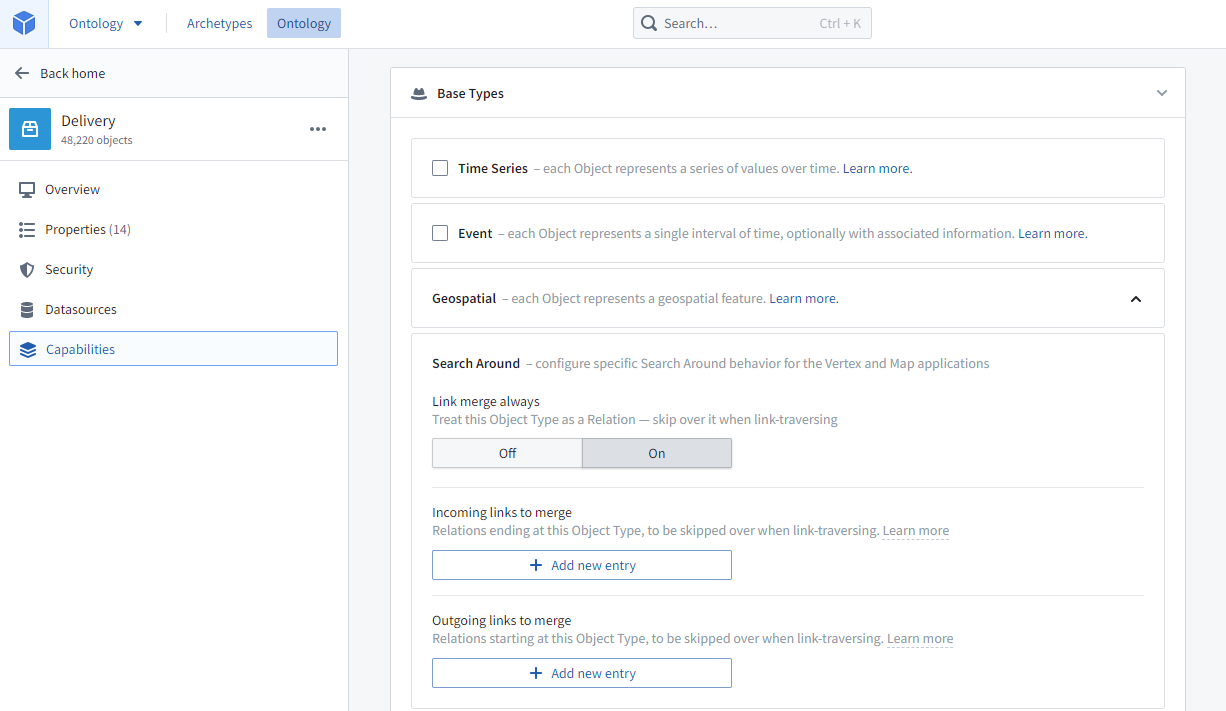
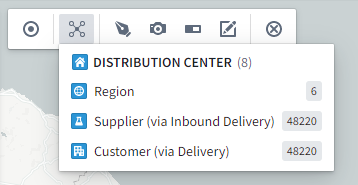
For example, if the intermediary object type is Delivery, and the object types on either side are Distribution Center and Customer, then when a Distribution Center is selected to Search Around on, Delivery will not show up in the list, but Customer (via Delivery) will. See below for an example:
Set specific link traversals to be link merged
To designate specific link traversals to be link merged, specify both the Incoming links to merge and Outgoing links to merge in the Search Around section of the intermediary object type's Capabilities tab.
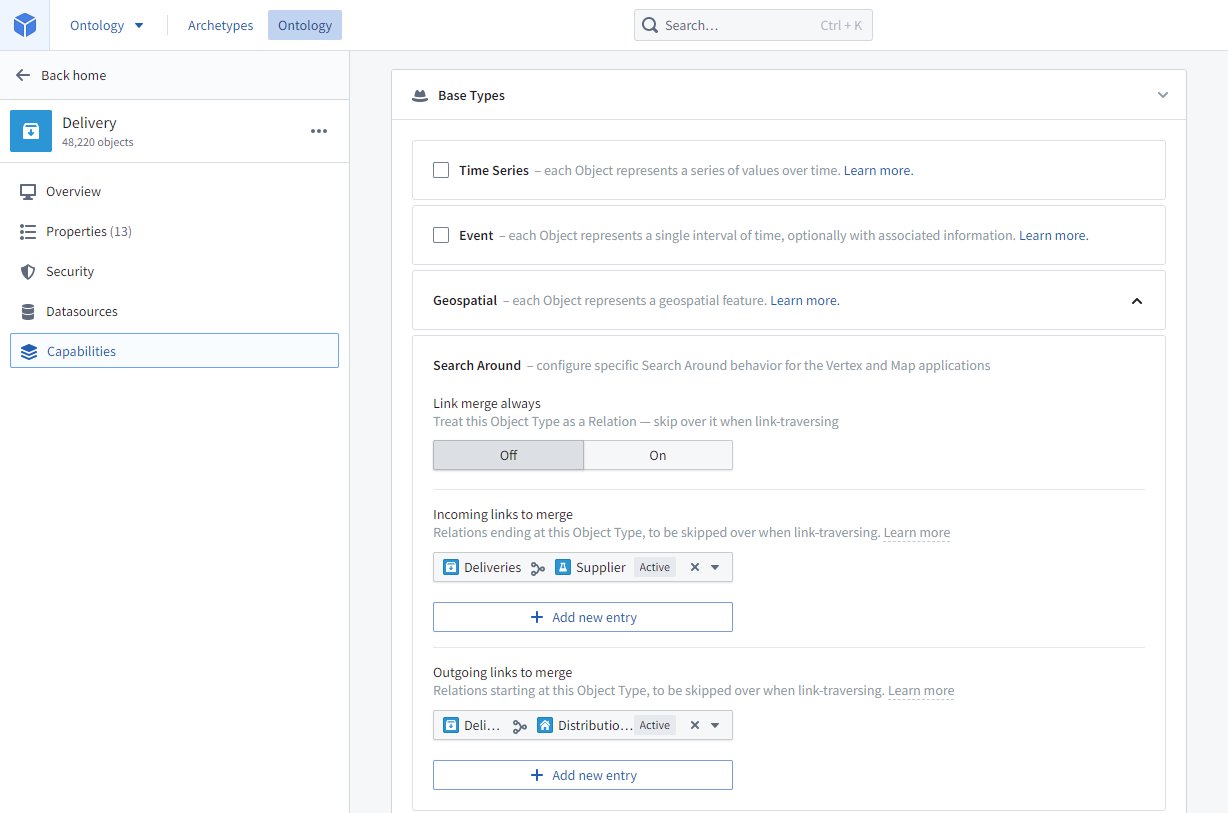
For example, if you want to be able to perform a Search Around from a Supplier object type to a Distribution Center object type via a Delivery object type, you would configure the Delivery object type as the intermediary by selecting the Delivery <-> Supplier link as Incoming links to merge and the Delivery <-> Distribution Center link as Outgoing links to merge. Now, when a Supplier is selected to Search Around on, Distribution Centers (via Delivery) will appear as an option in the list.
If you want both link traversal directions to appear in the Search Around list (for example, for both Suppliers to have Distribution Centers (via Delivery) and also Distribution Centers to have Suppliers (via Delivery)), you will need to configure those links as both Incoming links to merge and Outgoing links to merge.
Search Around functions
You can create powerful Map Search Arounds for the Map by writing Map Search Around functions. This allows you to write TypeScript functions that are given the selected objects and traverse the Ontology to bring back all the objects that are relevant or useful for the specific analysis being undertaken.
Map Search Around functions return a data structure that can include:
objectRids: Objects, which will be added to the map.edges: Edges, which include a source object, a target object, and optionally intermediary objects. The source and target objects will be added to the map with an arc drawn between them, and the intermediary objects will be listed when the arc is selected.measures: Time Series Measures, which will be added to the timeline.
Implement a Map Search Around function
Map Search Around functions are developed in a TypeScript functions repository. For more information, see the Functions documentation.
Return type
A Map Search Around function must declare a return type of Promise<IMapSearchAroundResults>. The Map application will discover Search Around functions using the name and structure of their return type, so the return type must be declared exactly as follows:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16export interface IMapSearchAroundResults { objectRids?: string[]; edges?: IMapSearchAroundEdge[]; measures?: IMapSearchAroundMeasure[]; } export interface IMapSearchAroundEdge { sourceObjectRid: string; targetObjectRid: string; intermediaryObjectRids?: string[]; } export interface IMapSearchAroundMeasure { objectRids: string[]; measureId: string; }
Parameters
Map Search Around functions must include one (and only one) object parameter, which can be one of the following:
- A single object: this Search Around function will be available in the Search Around menu when a single object of the specified type is selected. For example:
Copied!1public exampleSearchAround(object: ExampleObjectType) { ...
- An object array: this Search Around function will be available in the Search Around menu when any number of objects of the specified type are selected. For example:
Copied!1public exampleSearchAround(objects: ExampleObjectType[]) { ...
- An object set: this Search Around function will be available in the Search Around menu when any number of objects of the specified type are selected. For example:
Copied!1public exampleSearchAround(objectSet: ObjectSet<ExampleObjectType>) { ...
Map Search Around functions can optionally include any number of additional parameters of these scalar types: string, boolean, Integer, Long, Float, Double, LocalDate, or Timestamp (see Scalar types for more details). When a user executes a Search Around function with additional parameters, the user will be prompted to enter values for the parameters. For example:
Copied!1public exampleSearchAround(objectSet: ObjectSet<ExampleObjectType>, stringParameter: string, timestampParameter: Timestamp) { ...
Tips & troubleshooting
- To maximize performance, all code should be as asynchronous as possible. In your function code, always use
allAsync()andgetAsync()instead ofall()andget()when loading objects, and use as fewawaitstatements as possible. - The Map application will use the latest published version of a function. To publish your Function, you need to tag the branch/commit you want with a semver-compatible version, for example: 1.0.0.
- Your repository needs access to all the Ontology objects and links you want to use in your function. This is configurable under the Ontology section of the Repository's Settings.
- If the object types and their backing datasets are defined in a different project than the repository, the project containing your repository will need a reference to the backing datasets and those object types.
Examples
This example code contains three Search Around functions, based on open-source sample data:
airportsRelatedObjects: Returns various objects related to a set of airports. Could be used in a map template for airport analysis.nearbyAirports: Performs a geospatial search to find other airports within a given distance. The function takes an optional distance parameter, allowing the user to provide a distance when executing the function.routesBetweenAirports: Given a set of airports, returns all routes just between those airports.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94import { Distance, Function, Integer, Filters } from "@foundry/functions-api"; import { ObjectSet, Objects, ExampleDataAirport } from "@foundry/ontology-api"; export interface IMapSearchAroundResults { objectRids?: string[]; edges?: IMapSearchAroundEdge[]; measures?: IMapSearchAroundMeasure[]; } export interface IMapSearchAroundEdge { sourceObjectRid: string; targetObjectRid: string; intermediaryObjectRids?: string[]; } export interface IMapSearchAroundMeasure { objectRids: string[]; measureId: string; } export class MapSearchAroundFunctions { /** * Return relevant objects for airports: runways, routes */ @Function() public async airportsRelatedObjects(airportSet: ObjectSet<ExampleDataAirport>): Promise<IMapSearchAroundResults> { const relatedObjects = (await Promise.all([ airportSet.searchAroundExampleDataRunway().allAsync(), airportSet.searchAroundRoutes().allAsync(), ])).flat(); const objectRids = relatedObjects.map(o => o.rid!); return { objectRids, }; } /** * Return all airports within the specific number of kilometres of the selected airport (defaulting to 50) */ @Function() public async nearbyAirports(airport: ExampleDataAirport, distanceKm?: Integer): Promise<IMapSearchAroundResults> { const point = airport.airportLocation; const distance = Distance.ofKilometers(distanceKm ?? 50); if (point === undefined) { return {}; } const nearbyAirports = await Objects.search() .exampleDataAirport() .filter(airportFilter => airportFilter.airportLocation.withinDistanceOf(point, distance)) .allAsync(); const objectRids = nearbyAirports.map(o => o.rid!); return { objectRids, }; } /** * Return only routes that depart from and arrive in the selected airports */ @Function() public async routesBetweenAirports(airportSet: ObjectSet<ExampleDataAirport>): Promise<IMapSearchAroundResults> { const airports = await airportSet.allAsync(); const airportCodes = airports.map(airport => airport.airport); const airportsByCodes = new Map(Array.from(airports, a => [a.airport, a])); const routes = await Objects.search() .exampleDataRoute() .filter(route => Filters.and( route.origin.exactMatch(...airportCodes), route.dest.exactMatch(...airportCodes), )) .allAsync(); const edges = routes.map(route => ({ sourceObjectRid: airportsByCodes.get(route.origin!)!.rid!, targetObjectRid: airportsByCodes.get(route.dest!)!.rid!, intermediaryObjectRids: [route.rid!], })); return { edges }; } }