- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Queries
Queries are the read-only subsets of functions that may be optionally exposed through the API gateway. They cannot have any side effects, such as modifying the Ontology or altering external systems. You should use an Action if you need those additional editing capabilities through the API gateway.
Query decorator
Use the following syntax to define a query function.
Copied!1 2 3import { Query } from "@foundry/functions-api"; @Query({ apiName: "myTypeScriptV1Function" })
Copied!1 2 3 4// Export a config object with an apiName parameter from the file containing the function export const config = { apiName: "myTypeScriptV2Function" };
Copied!1 2 3from functions.api import function @function(api_name="myPythonFunction")
For Python and TypeScript v1 functions, the decorator accepts an API name parameter of type string, which is required to define an API name. When using TypeScript v1, the query will behave similarly to the existing @Function decorator if the apiName parameter is not defined. Note that the corresponding Python syntax is api_name.
Example: API-named query
The example below demonstrates how to expose a query through the API gateway:
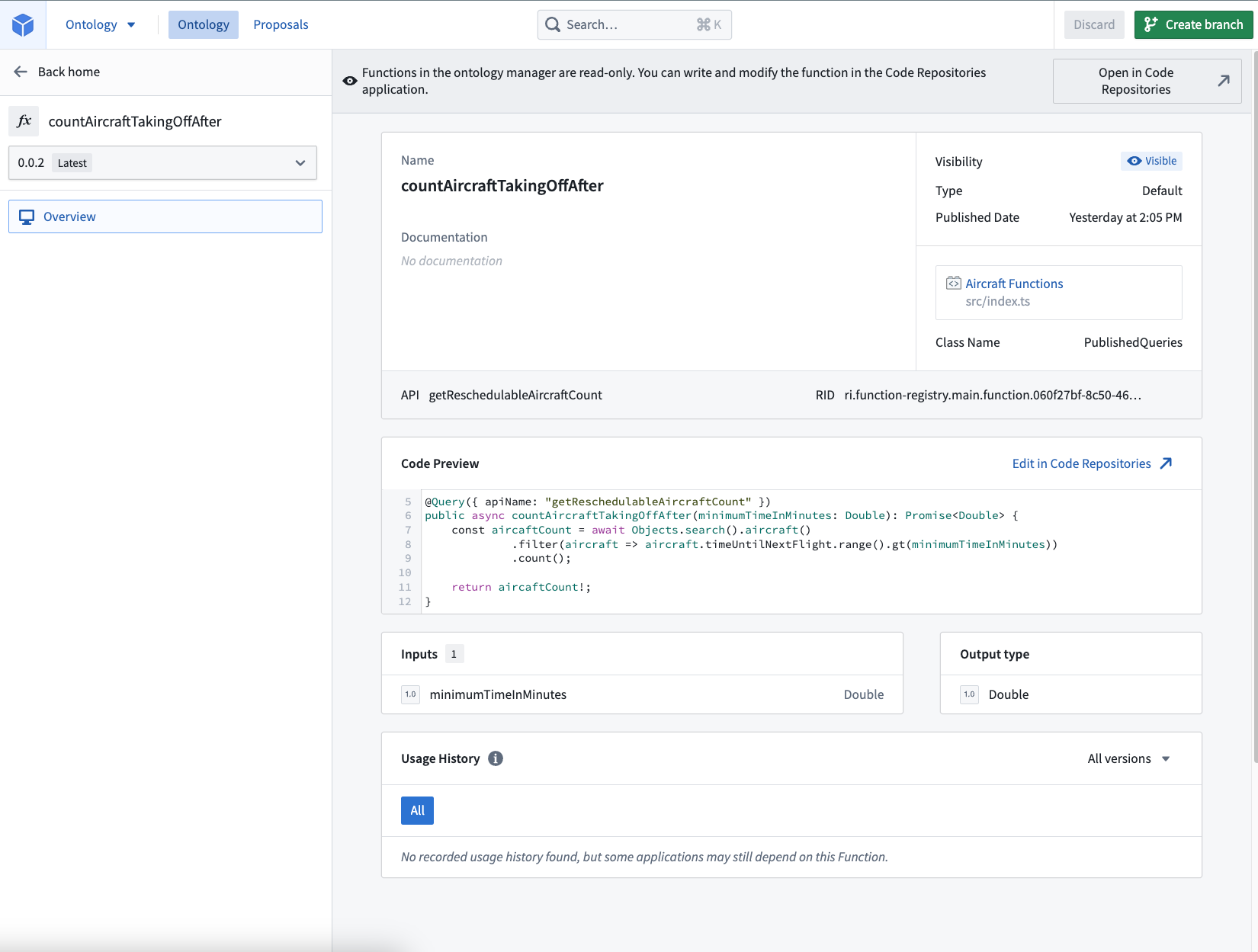
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13import { Query, Double } from "@foundry/functions-api"; import { Objects, Aircraft } from "@foundry/ontology-api"; export class PublishedQueries { @Query({ apiName: "getReschedulableAircraftCount" }) public async countAircraftTakingOffAfter(minimumTimeInMinutes: Double): Promise<Double> { const aircaftCount = await Objects.search().aircraft() .filter(aircraft => aircraft.timeUntilNextFlight.range().gt(minimumTimeInMinutes)) .count(); return aircaftCount!; } }
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19import { Client } from "@osdk/client"; import { Double } from "@osdk/functions"; import { Aircraft } from "@ontology/sdk"; export const config = { apiName: "getReschedulableAircraftCount" }; async function countAircraftTakingOffAfter(client: Client, minimumTimeInMinutes: Double): Promise<Double> { const { $count } = await client(Aircraft).where({ timeUntilNextFlight: { $gt: minimumTimeInMinutes } }).aggregate({ $select: { $count: "unordered" } }) return $count; } export default countAircraftTakingOffAfter;
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12from functions.api import Double, function from ontology_sdk import FoundryClient from ontology_sdk.ontology.objects import Aircraft @function(api_name="getReschedulableAircraftCount") def count_aircraft_taking_off_after(minimum_time_in_minutes: Double) -> Double: client = FoundryClient() aircraft_count = client.ontology.objects.Aircraft.where( Aircraft.time_until_next_flight > minimum_time_in_minutes ).count().compute() return aircraft_count
API name validations
The apiName of a query must be a string that meets the following requirements:
- Be in
lowerCamelCase. - Be under 100 characters.
- Not contain leading numbers.
- Be unique among all Ontologies imported into the repository.
- The tagging process will fail if the
apiNameis not unique, requiring you to change the name.
- The tagging process will fail if the
Additionally, a repository containing API-named queries must import entities from at least one ontology.
Version and update API-named queries
API-named queries will always use the latest tagged version of the published query and do not follow the same semantic versioning paradigm as other Foundry functions.
To disassociate the API name from the query and break it in the API gateway, you must remove the API name from the query decorator and release a new tag from the repository.
Changing the API name in the decorator and publishing a new tag will break the consumer. Only the latest published version of the query is supported.
To allow consumers to upgrade at their convenience without breaking changes, you can support multiple versions of the same API name. To do this, you must make a copy of the query code in your repository and give it a different API name, for example getReschedulableAircraftCountV2.
Search and view queries
As with other functions, you can search for and manage your queries in Ontology Manager. You can search for the query name or the API name. In the example above, the queries are getReschedulableAircraftCount for the API name and countAircraftTakingOffAfter for the query name, respectively.
When using TypeScript v1 functions, you may need to update the functions.json file in your repository to enable queries by setting the enableQueries property to true:
Copied!1 2 3{ "enableQueries": true }
Call a query function
After publishing your TypeScript or Python query function, navigate to the code repository where you want to consume the function, and import it using the Resource imports sidebar.
Your function will be callable from the consuming repository. For example:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8import { Queries } from "@foundry/ontology-api"; export class MyFunctions { @Function() public callQueryFunction(): Promise<Double> { return Queries.getReschedulableAircraftCount(10); } }
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9import { Client } from "@osdk/client"; import { Double } from "@osdk/functions"; import { getReschedulableAircraftCount } from "@ontology/sdk"; async function callQueryFunction(client: Client): Promise<Double> { return client(getReschedulableAircraftCount).executeFunction({ timeUntilNextFlight: 10 }); } export default callQueryFunction;
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8from functions.api import Double, function from ontology_sdk import FoundryClient @function def call_query_function() -> Double: return FoundryClient().ontology.queries.get_reschedulable_aircraft_count( time_until_next_flight=Double(10) )
For TypeScript v1 functions, Foundry must know which query functions you call from a published function. We automatically provide static analysis to try and detect queries that are called. However, this static analysis may occasionally miss certain calls leading to a runtime error instructing you to add the @Uses decorator. This decorator serves to augment the automatically detected query usage.
The following example demonstrates the usage of the @Uses decorator:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10import { Uses } from "@foundry/functions-api"; import { Queries } from "@foundry/ontology-api"; export class MyFunctions { @Uses({ queries: [Queries.getReschedulableAircraftCount] }) @Function() public callQueryFunction(): Promise<Double> { return Queries.getReschedulableAircraftCount(10); } }