Add functions to a Marketplace product
Use Foundry DevOps to include your functions in Marketplace products for other users to install and reuse. Learn how to create your first product.
Supported features
DevOps packages functions for installation and reuse but does not provide user-viewable source code for TypeScript V1 functions. This means that after installation, you will be able to use the installed TypeScript functions, but you will not be able to view their source logic; the repository accompanying the function will be empty.
Python and TypeScript V2 functions do include user-viewable source code in the Marketplace product. However, the contents of the functions still cannot be edited after installation when installed in production mode.
Adding functions to products
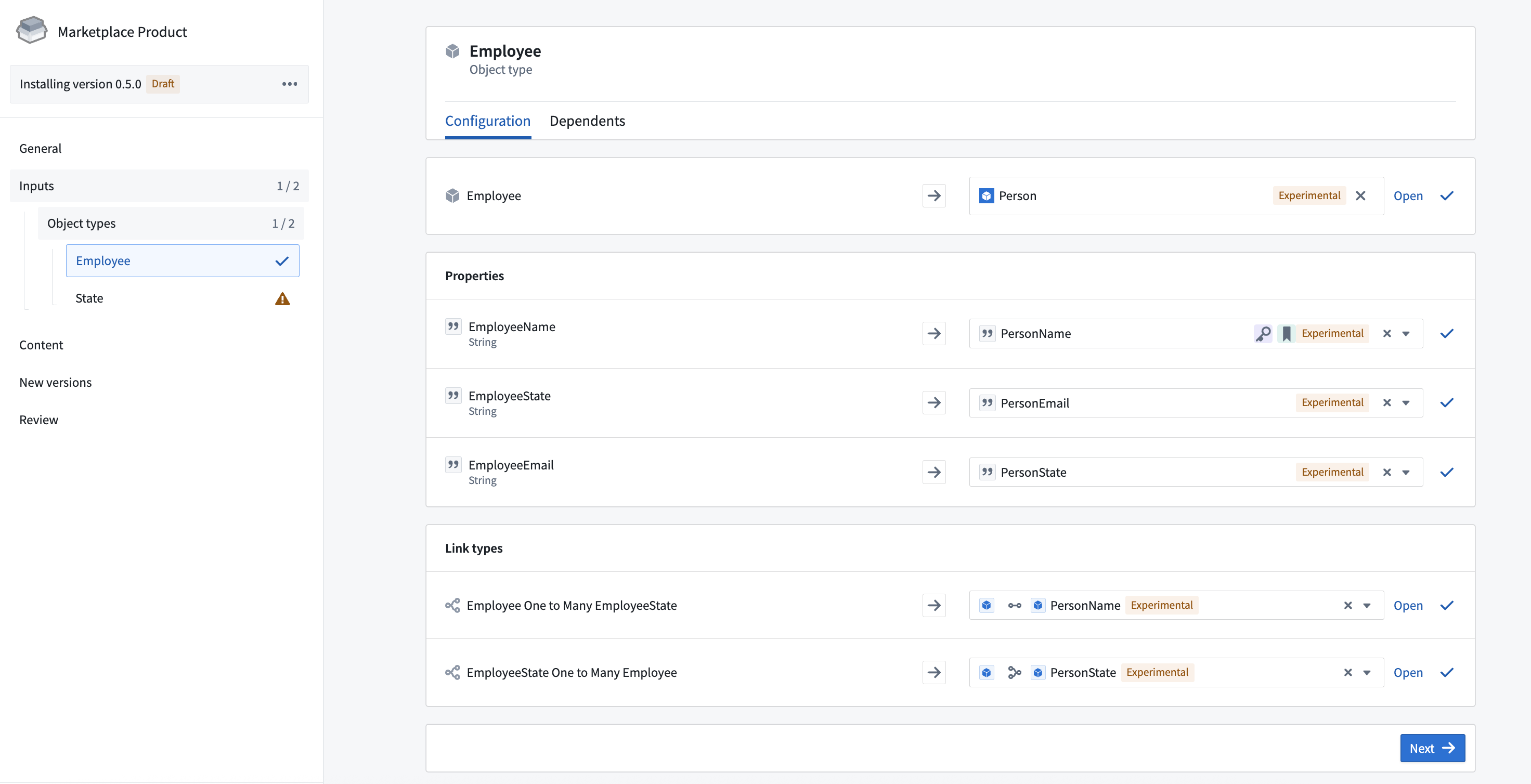
To add a function to a product, create a product. Then, add a Function output as shown below.
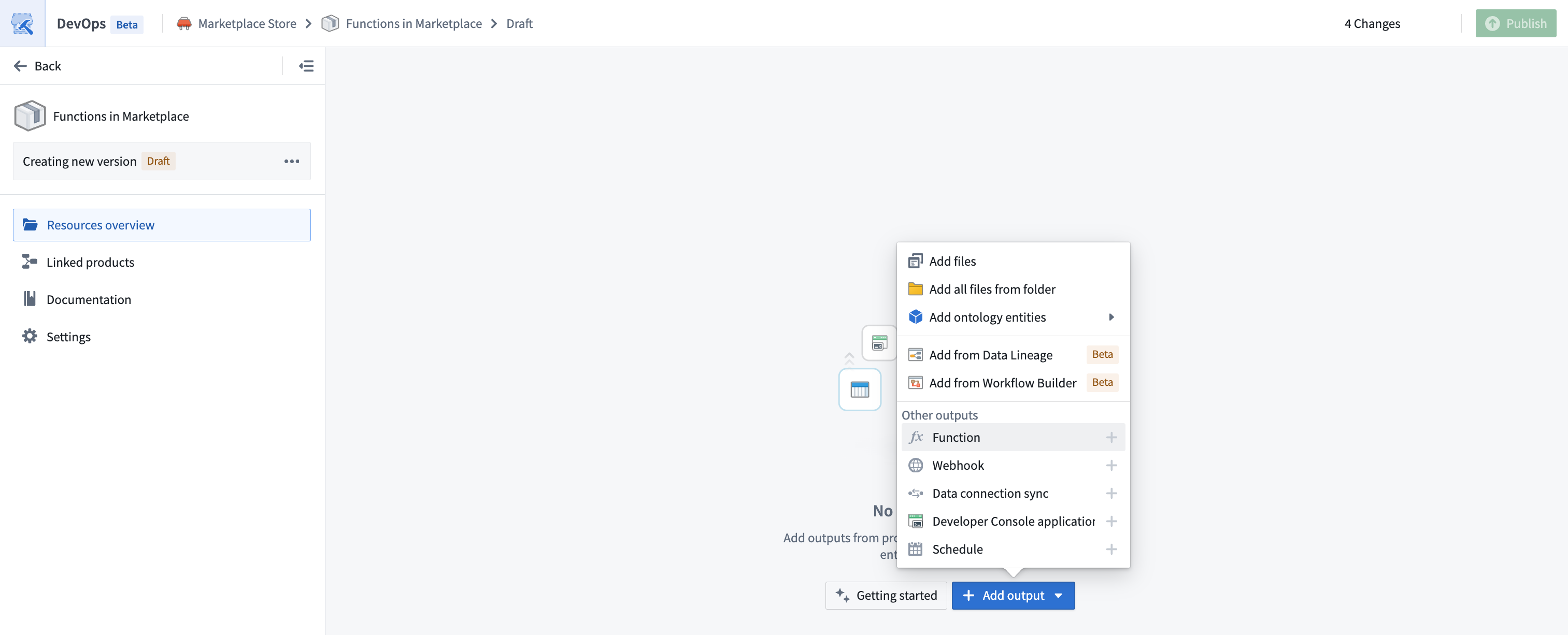
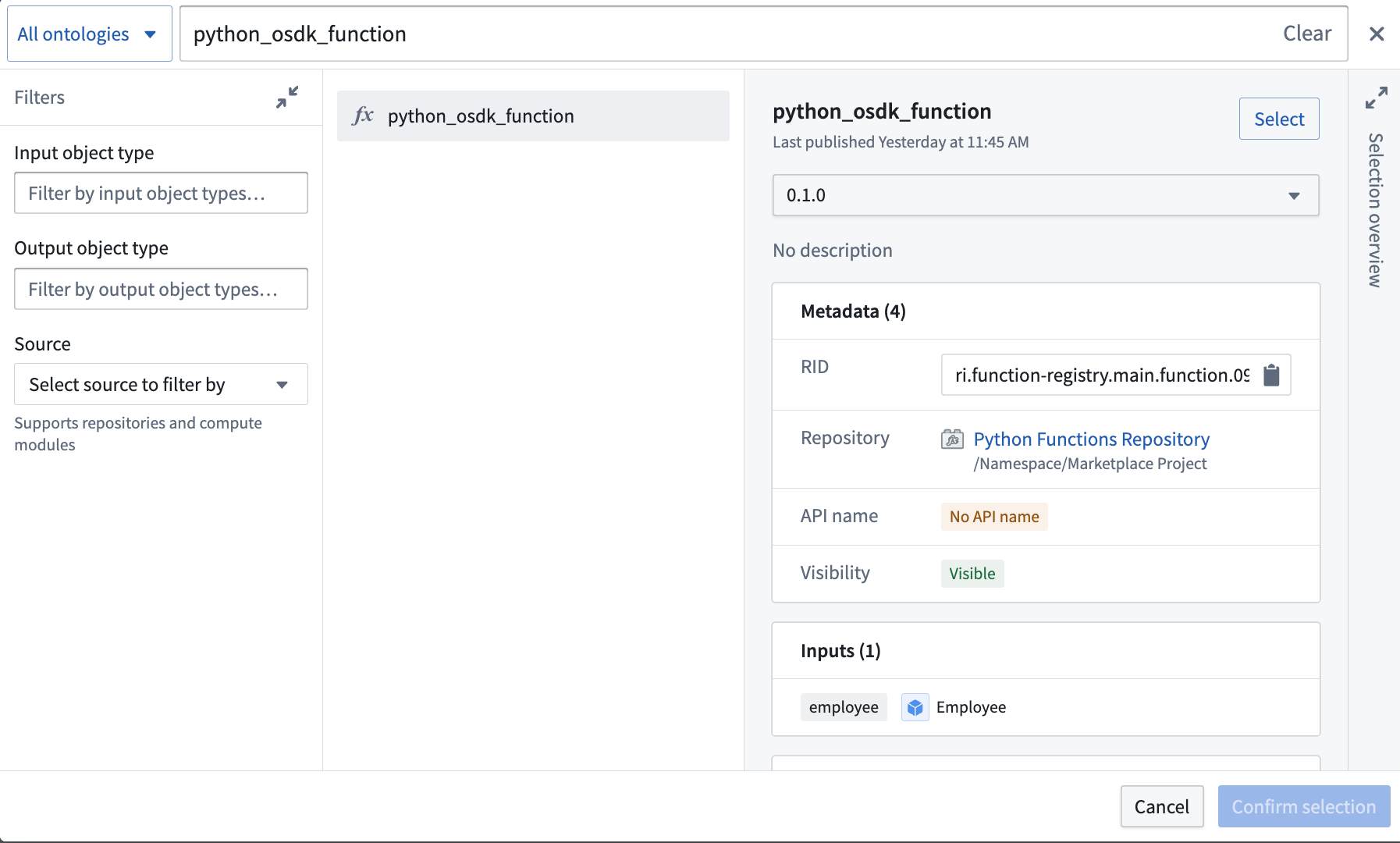
You will then be prompted to choose a function and a version. In most cases, you should select the latest version of a function.
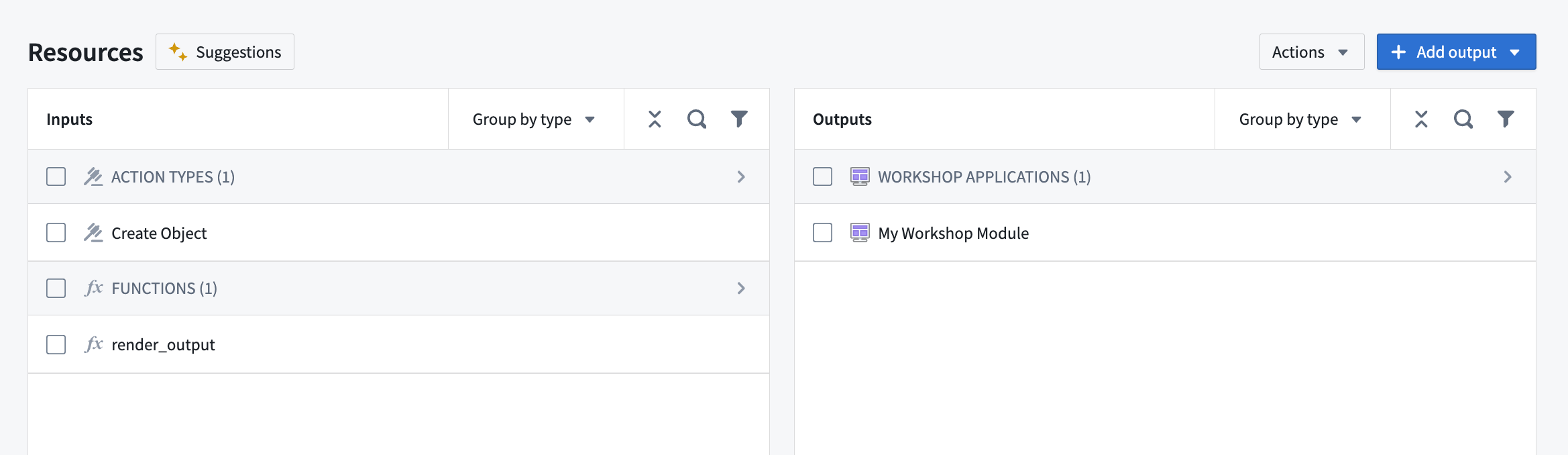
While you can select functions directly, we recommend first adding content such as Workshop applications; the functions these resources require will be automatically added as inputs to your product.
Use OSDK functions in Marketplace products
Python and TypeScript V2 functions that use OSDKs can also be packaged as outputs in Marketplace products. When you add a function that uses an OSDK as an output to your Marketplace product, the OSDK will also be added as an output while the ontology entities used in your OSDK will be added as inputs.
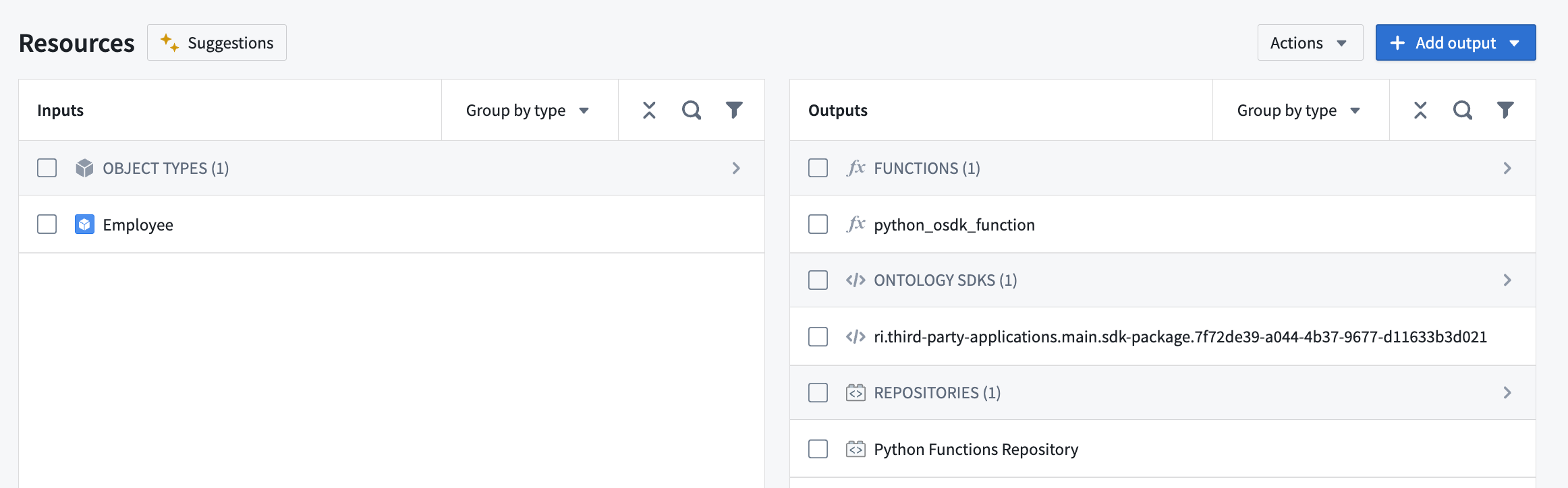
Users who install your Marketplace product will then be able to remap the objects, links, and other ontology entities referenced in your OSDK to refer to entities in the ontology where the product is being installed.
When the function is executed after installation, it will automatically use the ontology entities that were configured during installation.
Function overrides at installation
Calling queries or making API calls within overridden static functions is not supported.
It is possible to modify parts of a function’s behavior at install time by providing a locally defined function which overrides the “static” function input that is shipped with your Marketplace product. To do this, you can specify that a particular function may be overridden by using the @Static decorator.
For example, consider a function that negates a given number:
// Normal function
import { Function, Double } from "@foundry/functions-api";
export class MyFunctions {
@Function()
public async modifyNumber(d: Double): Promise<Double> {
return -d;
}
}
To make this function overridable, rewrite it as follows:
// Overridable function
import { Function, Static, Double } from "@foundry/functions-api";
export class MyFunctions {
@Function()
public async modifyNumberByStaticFoo(
n: Double,
@Static() staticFunctionInput: (num: Double) => Promise<Double> = this.defaultFoo
): Promise<Double> {
return await staticFunctionInput(n);
}
private async defaultFoo(n: number) {
return -n;
}
}
When packaging a static function, inputs will appear as staticFunctionInputs during installation, as shown below. Installers can then provide their own function logic that will override the default behavior. Conceptually, the staticFunctionInputs serve as function input parameters to the overridable function.
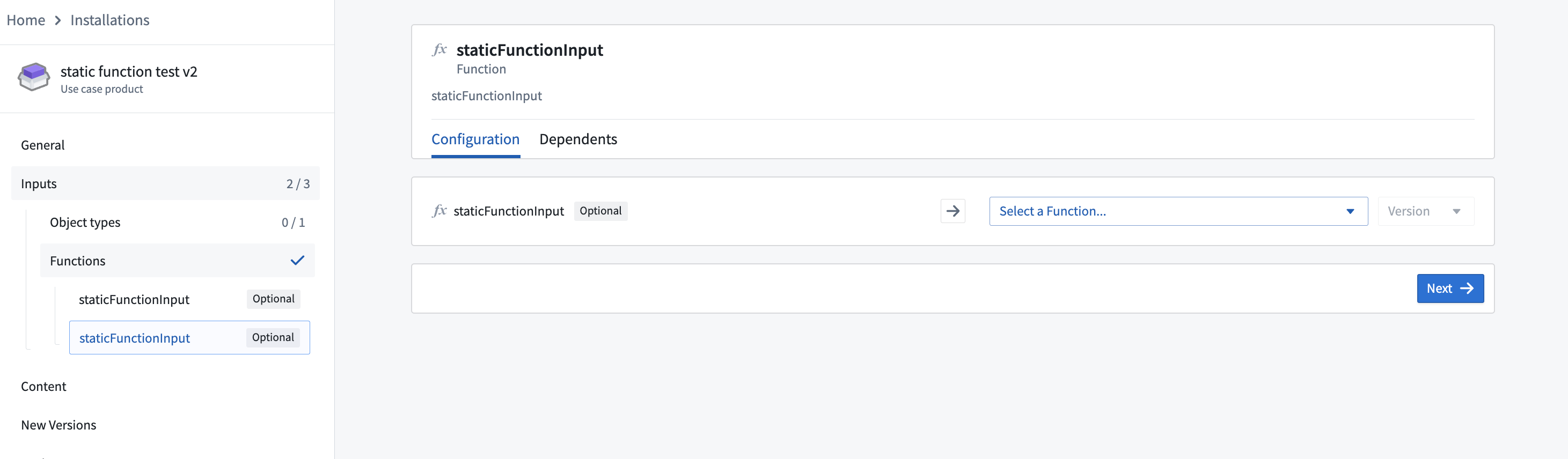
For example, you may have a supply chain optimization function whose logic needs slight adjustments in another context. To allow this, specify that the function is overridable before packaging it, and then override it during installation.